Oral infections are among the many reasons people visit the dentist for treatment. There are a number of them that people suffer from. These infections can be serious, affecting daily activities and the overall quality of life. I will be discussing some of the common oral infections, their respective causes and the available treatment options.
1. Gingivitis
Gingivitis is a common oral infection. It refers to the inflammation of the gums. Inflamed gums will be puffy, reddish and bleed easily. People with gingivitis may bleed from the gums while brushing.
Causes
Buildup of plaque on the teeth and gums causes gingivitis. Plaque is a biofilm that houses different microorganisms (majorly bacteria) that are destructive to the teeth and gums. Dental plaque is the primary cause of dental problems such as dental caries, gingivitis and periodontal problems.
When plaque hardens, it forms calculus. Dental calculus or tartar is that hard yellowish to greenish-black substance that builds from around the neck of the tooth. It creates a surface for more plaque to adhere to.
One interesting thing about dental calculus is that it is not removable by brushing, notwithstanding how hard you try.
In addition to gingivitis, calculus causes gum recession and bad breath.
Treatment
First and foremost, if you notice signs of gingivitis, visit your dentist for treatment to prevent complications that may arise from this oral infection.
A scaling and polishing procedure will be carried out to remove plaque and calculus that are causing the gum inflammation.
After professional teeth cleaning you should do warm saline mouth bath. Warm saline rinse is very effective in the healing of inflamed gums.
Lastly, you must make a commitment to improve your oral hygiene by brushing twice daily and flossing at least once a day.
2. Periodontal Diseases
They consist of inflammation affecting the supporting (periodontal) structures of the teeth. They are also called periodontitis. Signs and symptoms of periodontitis include periodontal pockets pain, shaky teeth, bleeding gums and bad breath. This group of oral infections is one of the common reasons people are seeking dental treatment.
Causes
Poor oral hygiene as a result of plaque and calculus buildup is the major cause of periodontitis.
Treatment
Once your dentist makes the diagnosis of periodontitis, they will offer the following treatment options for the oral infection.
A scaling and polishing procedure will be first carried out.
If there is any gum (periodontal) pocket, it will be cleaned out using specialised instruments.
After the treatment, your dentist will place you on antibiotics and analgesics.
your dentist may prescribe antiseptic mouth rinse and/or warm saline mouth bath.
3. Dental Caries
Dental caries or tooth decay is an infection of the teeth that is caused by certain bacteria within the oral cavity, the treatment of which depends on the extent of the decay.
tooth decay is the commonest oral health disease. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), dental caries in the permanent teeth is the most common health condition.
Causes
Four factors must interact sufficiently for dental caries to occur. They include:
A susceptible tooth surface or tooth at risk
bacteria : Streptoccoccus mutans
Diet. in this case food containing refined sugar or fermentable carbohydrate
Time is another important factor in the formation of dental caries. There must be sufficient time for bacteria to act on the fermentable sugar.
Treatment
The treatment choice for dental caries is determined by the extent of the decay. If the oral hygiene is poor, a professional teeth cleaning will be done first.
The tooth or teeth with decay can be filled if the decay has not reached the pulp chamber.
Where dental caries has extended into the pulp, it will result in the inflammation of the pulp (pulpitis). A root canal therapy is usually done, especially if the pulpitis is irreversible.
In cases where the tooth is unrestorable, tooth extraction is the treatment choice to eliminate the oral infection. After tooth extraction, there should be a plan for the replacement of the missing tooth.
4. Oral Thrush
Oral thrush or oral candidiasis is a fungal infection caused by a group of organisms known as Candida. It is generally seen in immunocompromised people such as people with HIV/AIDS, those at the extremes of age such as the aged and babies, those on long term systemic steroids or antibiotics.
Oral thrush is a milky white or yellowish patch on the surface of the tongue, cheek, lips. Oftentimes, the white patches can be wiped off, leaving a reddish or bleeding surface. It can sometimes cause a burning sensation making eating quite difficult.
Causes
Candida is a group of fungi that causes oral candidiasis. An example is the Candida albican. It is a naturally occurring and the most abundant fungus on the body including the mouth.
Oral thrush is not common among immunocompetent individuals. It is common among the aged and babies as their immune system may not be strong enough to fight the infection. Denture wearers who have poor denture care may also suffer from oral candidiasis.
It also occurs if the body’s immunity is low. For example, cases of HIV/AIDS, chronic systemic diseases like uncontrolled diabetes melitus, and in individuals on long term antibiotics or immunosuppressive drugs.
Treatment
Antifungal medications are used in the treatment of oral thrush. These medications have both formulations for topical and systemic uses.
5. Aphthous Ulcers
These are small inflammatory and painful oval shaped sores on the gums, tongue, cheek, lip or on the roof of your mouth. These sores cause severe pain, making it hard to eat. Most aphthous ulcers resolve on their own within 1-2 weeks.
The presence of food in the mouth, especially hot and spicy foods worsens the pain.
Causes
The cause(s) of aphthous ulcer are unknown. However, certain risk factors do exist. They include the following:
- Heredity.
- Deficiency of vitamin B12, iron and folic acid.
- Hormonal changes
- Stress
- Trauma
- Food allergies (to nut, gluten)
Treatment
Treatment depends on the severity of the case.
Mild cases may not need systemic medications. A simple oral rinse like 5% tetracycline mouth rinse, chlorhexidine rinse to keep the sores clean and promote healing should be enough.
Topical anaesthetic gel or spray to ease pain during eating and analgesics can suffice for moderate cases.
However, in severe cases, corticosteroids can be added in addition to the topical treatment.
Individuals suffering from canker sores should also avoid hot and spicy foods.
Toothpastes containing sodium lauryl sulphate can also irritate oral ulcers and trigger pain.
6. Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease
This is a common childhood disease, usually affecting children under 5 years of age. It is a contagious disease that produces maculopapular rashes on the hand and feet. Hand foot and mouth disease also causes fever, skin rashes and mouth sores. It is self limiting, resolving within 10 to 14 days.
This oral infection can spread from one person to another. Common means of spreading it is through droplets from sneezing and coughing, direct contact with the fluid from blisters, and touching objects and surfaces that have the virus.
Cause
Coxsackie A virus causes hand, foot and mouth disease.
Treatment
This is one of the oral infections that can resolve on its own within 7 to 14 days, and may not require treatment in the hospital. However, there are certain things that can help someone suffering from hand, foot and mouth disease. They are:
Drinking water regularly
Use of paracetamol or ibuprofen to relieve pain.
Ease pain that worsens during eating by numbing the oral mucosa using lidocaine gel.
Individuals with this oral infection should be on a soft diet until infection resolves.
If infection persists after 14 days, kindly consult your physician or dentist.
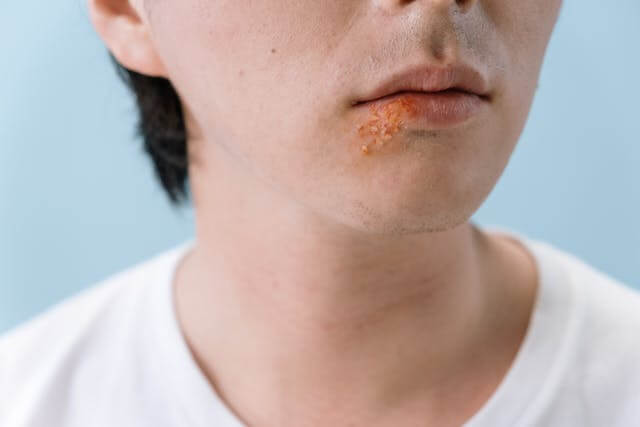
7. Oral Herpes
Oral herpes, herpes labialis or cold sore is a common oral infection that can spread from one person to another. According to the National Institute of Health, 50 percent to 80 percent of adults in the US have oral herpes.
Most people don’t show symptoms after contracting HSV-1. Some others only have mild symptoms. Symptoms include:
- Pain or burning sensation in the mouth
- Oral blisters or sores
- There could be headache and fever,
Causes
Herpes simplesx virus type-1 (HSV-1) causes oral herpes. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), about 3.8 billion people under 50 years of age have HSV-1 globally.
The infection can spread from direct exposure to infected body fluid like saliva or droplets from an active sore.
Oral herpes also spreads through kissing and contact with droplets on beddings.
Treatment
Antiviral drugs are employed in the treatment of oral infection caused by HSV-1. Common antiviral drugs include acyclovir and famciclovir.
Pain medications such as paracetamol and ibuprofen helps to relieve pain.
Conclusion
The treatment of oral infections depends on the causes. While some are self limiting and may not require medications, it is important to see a dentist when an individual has symptoms suggestive of oral infections.